Ready to proof -- Clare 2/8/22
KJ proofed on 2/9 and sent corre
Revised on 2/9
Ready for
DID YOU KNOW?

How Does pH Impact the Polymerization of Functional Monomers?
Video credit: ilyast / Creatas V1ideo, via Getty Images
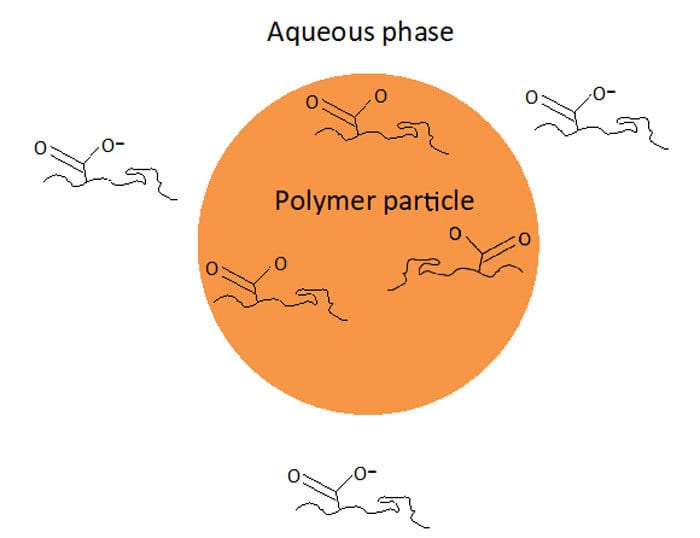
Most emulsion polymerization formulations include ~1-3% of a functional monomer such as acrylic, methacrylic or itaconic acid. Typically acid functional monomers are used, although for some products basic monomers such as DMAEMA (dimethyl aminoethyl methacrylate) are also used in some applications. What do all of these monomers have common? They all contain functional groups that can exist in either a neutral or charged state, depending on the pH of the latex. Acid monomers exist in an anionic form at neutral or basic pH, while basic monomers exist in a cationic form at neutral or acidic pH.
Understanding this behavior is critical to ensuring the functional monomer ends up where it is supposed to be, ideally on the surface of the particle where it is able to provide additional colloidal stability to the latex. However if the reaction conditions are not carefully selected and controlled, it is possible for much, or even most, of the functional monomer to end up in the aqueous phase as water-soluble polymer or oligomer.
How do you know what pH range to select to ensure functional monomer resides on the particle surface? Although in the final product we want the functional monomer to be in its charged state to make the latex more stable, somewhat paradoxically we want the functional monomer to be in its neutral state during the emulsion polymerization. In its neutral state the monomer is relatively more hydrophobic and therefore partitions better into the particle and has a chance to polymerize at or near the surface; in its charged state the monomer is more likely to form polymer in the aqueous phase.
For most acid monomers, the ideal polymerization pH range is typically around 2-3, while for many basic monomers a pH range of about 9-10 is usually more suitable. However these values depend on the particular monomers you are using, and a detailed understanding of the pH chemistry is required. Only when the polymerization is complete is the latex pH changed to ionize the functional groups and provide additional latex stability. With acid monomers, pH is adjusted to about 8-9.
This subject is treated in detail in several of our STEP’n workshops. We welcome comments and further discussion of this topic. Please contact us via our website www.epced.com.

The “Did You Know….?” series is a bi-monthly note from Emulsion Polymers Consulting and Education (EPCEd) that is intended to present simple questions about topics that are important to those working in the emulsion polymers area. Short and concise answers to those questions are presented to educate readers and to elicit comments and further discussion. Some readers will already know the answers and be familiar with the topic, while others, especially those newer to the field, will benefit from the answers and discussion. Experienced practitioners may also find new insights in the discussion. Paint & Coatings Industry magazine has partnered with EPCEd to share the “Did You Know” notes with our readers throughout the year.
